Shock and awe is “a military strategy based on the use of overwhelming force and spectacular displays of power to paralyze the enemy’s perception of the battlefield and destroy its will to fight”. Donald Trump started his term by issuing the executive orders he had promised in his campaign.
Trump ordered the suspension of federal grants and loans and a pay freeze, the abolition of DEI programs in the federal government, the creation of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), the declaration of a national emergency on the Mexican border, the revocation of birthright citizenship for certain immigrant children and withdrawal from the Paris Climate Agreement, declared an energy emergency and suspended the Green New Deal, withdrew United States from the World Health Organization, suspended the law banning TikTok, and announced various economic and artificial intelligence initiatives. The execution of some of the decisions was halted at least temporarily by the courts.
Trump demanded that NATO members spend at least 5 percent on defense and threatened to take control of the Panama Canal and Greenland. Trump also imposed high import tariffs on Canada, Mexico and China and threatened that Europe would be next.
Equity market performance erratic in the US
The S&P 500 index got off to a weak start in January but managed to turn around and gain 3 percent by the end of the month. Trump’s inauguration and US banks’ strong results boosted sentiments.
Nvidia’s price was hit hard when Chinese start-up DeepSeek released its powerful and low-cost AI that challenged the need for expensive semiconductors. Nvidia’s share price plummeted 17 percent after the news. The company will publish its results on February 26. Microsoft, Meta and Apple beat earnings expectations, while Tesla lagged behind. The prices of these stocks were volatile after the earnings reports.
Steady positive development was finally seen on European stock markets. The Stoxx index had its best month in two years, rising 6.5 percent.
The rise in long-term interest rates eased in January. The US ten-year rate rose by 0.3 percentage points to 4.8 percent, but eventually settled back at the year-end level. The German 10-year rate followed the US rate, but did not fall as much. Federal elections will be held in Germany on February 23 and the right-wing parties are expected to win.
The US Federal Reserve kept its policy rate unchanged, as anticipated. The European Central Bank cut its policy rate by 0.25 percentage points, as anticipated. In the US, expectations of monetary easing have faded, but the ECB is expected to continue lowering its interest rates towards 2 percent.
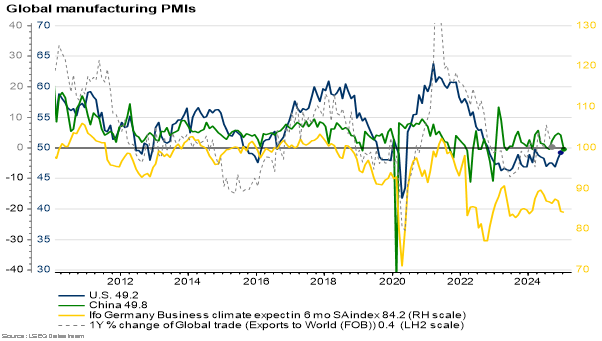
Economic outlook remains optimistic
In the US, employment and industrial confidence improved. In the euro area, economic growth remained weak in late 2024 and consumer confidence went into decline. The Chinese economy grew faster than expected at end of the year, exceeding its 5 percent target. Chinese companies’ outlooks weakened, however.
The new US administration’s policies are widely considered to benefit US companies and the US economy. The primary concern is the impact of possible import tariffs on consumer prices and on the economies of countries exporting to the US. The IMF forecasts global economic growth of +3.3 percent this year.
Figure: Industrial outlooks in the US, China and Germany